Sterilization of medical devices is a critical process integral to ensuring patient safety and preventing healthcare-associated infections. Medical devices come into direct contact with patient’s body or bodily fluids, making them potential vectors for the transmission of harmful pathogens if not properly sterilized. Therefore, sterilization is essential to eliminate microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, from medical devices before their use in clinical settings.
Sterilization refers to the complete destruction or removal of all viable microorganisms, including their spores, from a surface, environment, fluid, or compound. The process aims to render medical devices free from infectious agents, thus reducing the risk of patient harm and cross-contamination.
Various sterilization methods are employed in healthcare facilities, each with its advantages, limitations, and compatibility with different types of medical devices. Common sterilization methods include steam sterilization (autoclaving), Ethylene Oxide (EO) sterilization, radiation sterilization (gamma, electron beam), and low-temperature sterilization methods such as hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and vaporized hydrogen peroxide.
The choice of sterilization method depends on factors such as the type of medical device, its material composition, complexity, and compatibility with specific sterilization processes. Manufacturers, healthcare facilities, and regulatory bodies collaborate to ensure that medical devices are effectively sterilized while maintaining their functionality and integrity.
In addition to selecting appropriate sterilization methods, it is crucial to adhere to established standards, regulations, and guidelines governing the sterilization of medical devices. These standards, such as ISO 13485 (Quality Management Systems for Medical Devices) and ISO 11135 (Ethylene Oxide Sterilization), provide comprehensive requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of sterilization processes.
Moreover, validation of sterilization processes is essential to demonstrate the effectiveness and consistency of the chosen method in achieving microbial kill. Validation involves conducting rigorous testing to confirm that the sterilization process consistently achieves the desired level of microbial reduction without compromising the device’s performance or safety.
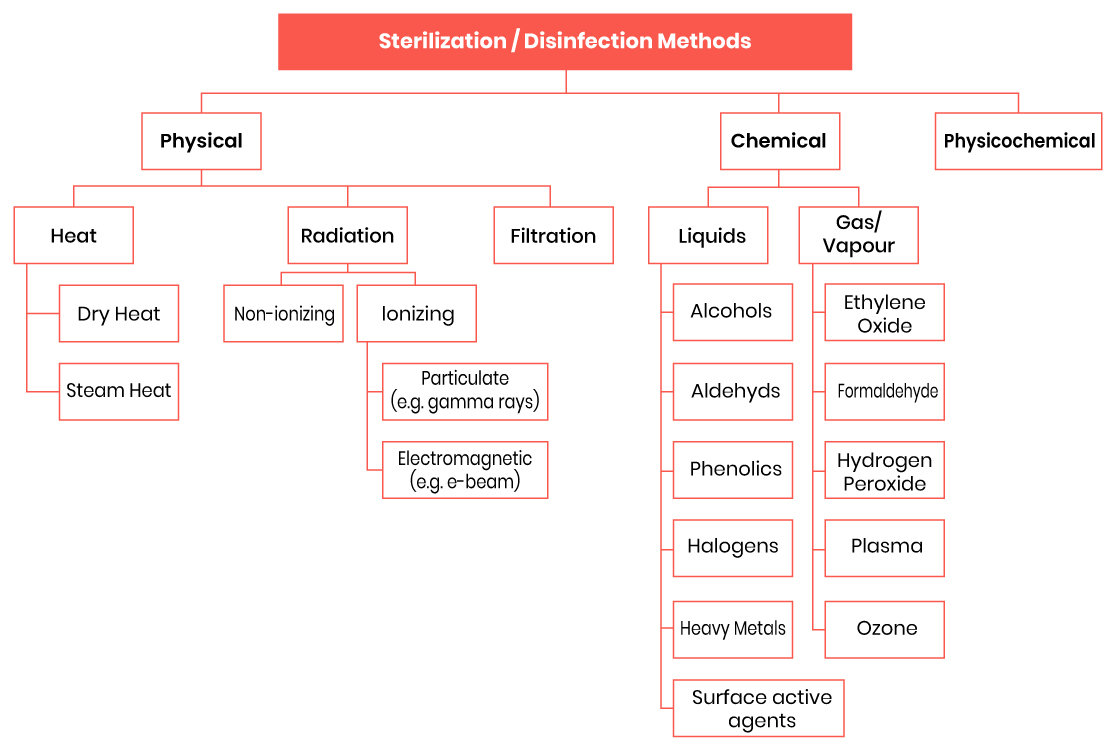 Figure 1: Various sterilization methods for Medical Devices
Figure 1: Various sterilization methods for Medical Devices
Overview of some common regulatory requirements and supporting standards:
Regulatory requirements for sterilization of medical devices are stringent due to the critical nature of these devices in patient care. The regulations and standards vary depending on the country or region, but some common requirements include:
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States:
The FDA regulates medical devices under the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, which includes the Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820). Part 820 outlines requirements for the design, validation, and control of manufacturing processes, including sterilization processes.
The FDA provides guidance documents such as “Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff – Reprocessing Medical Devices in Health Care Settings: Validation Methods and Labeling” and “Use of International Standard ISO 10993-1”.
- European Union:
Medical device sterilization is regulated under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or the In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Regulation (IVDR), depending on the classification of the device.
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards are harmonized with EU regulations. For sterilization, relevant standards include ISO 13485 for quality management systems and ISO 14937 for the validation and routine control of sterilization processes.
- International Standards:
ISO 11135: This standard specifies requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of ethylene oxide sterilization processes for medical devices.
ISO 11137: This standard specifies requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of radiation sterilization for medical devices.
ISO 17665: This standard specifies requirements for moist heat sterilization processes for medical devices.
- Additional Requirements:
Validation: Sterilization processes must be validated to demonstrate effectiveness and consistency. This typically involves performing validation studies to establish parameters such as time, temperature, and pressure for the sterilization process.
Biocompatibility: Medical devices must be biocompatible, meaning they do not cause harm to the patient. This is typically assessed through biocompatibility testing according to ISO 10993.
Labeling: Manufacturers must provide an adequate labeling for sterilized medical devices, including instructions for use, sterilization method, and any precautions or warnings.
Post-market Surveillance: Manufacturers are required to monitor the performance of sterilized medical devices after they have been placed on the market to identify and address any issues that may arise.
Adherence to these regulatory requirements and standards are essential for manufacturers to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and quality of sterilized medical devices. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in regulatory action, including product recalls and legal penalties.
Globally Recognized some key standards:
Several standards govern the sterilization of medical devices, ensuring their safety and efficacy.
- ISO 13485:2016 – Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes:
This standard specifies requirements for a quality management system specific to the medical devices industry, including those related to sterilization processes.
- ISO 11135:2014 – Sterilization of health care products – Ethylene oxide – Requirements for the development, validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices:
ISO 11135 specifies requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of ethylene oxide sterilization processes for medical devices.
- ISO 11137-1:2015 – Sterilization of health care products – Radiation – Part 1: Requirements for development, validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices:
This standard specifies requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of radiation sterilization processes for medical devices.
- ISO 17665-1:2006 – Sterilization of health care products – Moist heat – Part 1: Requirements for the development, validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices:
ISO 17665 specifies requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of moist heat sterilization processes for medical devices.
- ISO 14937:2009 – Sterilization of health care products – General requirements for characterization of a sterilizing agent and the development, validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices:
This standard provides general requirements for the characterization of a sterilizing agent and the development, validation, and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices.
- ANSI/AAMI ST79:2017 – Comprehensive guide to steam sterilization and sterility assurance in health care facilities:
This American National Standard provides guidance on steam sterilization and sterility assurance in healthcare facilities, including processes, monitoring, and documentation.
- ANSI/AAMI/ISO 11137-2:2013 – Sterilization of health care products – Radiation – Part 2: Establishing the sterilization dose:
This standard specifies methods for establishing the sterilization dose (the amount of radiation required for sterilization) for medical devices using radiation.
- ANSI/AAMI/ISO 17665-1:2006 – Sterilization of health care products – Moist heat – Part 1: Requirements for the development, validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices:
This standard, adopted from ISO, specifies requirements for the development, validation, and routine control of moist heat sterilization processes for medical devices.
These standards provide guidelines and requirements for various sterilization methods, including ethylene oxide, radiation, and moist heat. They cover the entire sterilization process, from development and validation to routine control and monitoring, ensuring that medical devices are effectively sterilized and safe for use in healthcare settings.
Conclusion:
Overall, sterilization of medical devices plays a pivotal role in safeguarding patient health, minimizing the risk of healthcare-associated infections, and upholding the quality and efficacy of medical treatments and procedures. By adhering to stringent sterilization protocols, healthcare professionals and manufacturers can uphold the highest standards of patient care and safety in clinical settings.
For any inquiries regarding Sterilization Regulatory Requirements, please contact MakroCare for expert guidance and support. Reach out to us today to discover more about the range of services we offer.